Research Themes
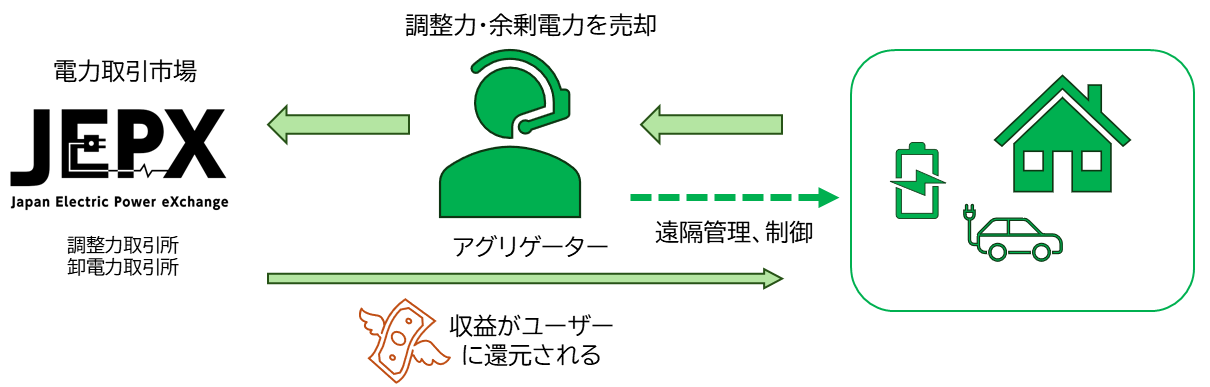
With the spread of renewable energy, the uncertainty of power generation and demand in the power system is increasing.Therefore, flexible energy control using storage batteries is attracting attention as the key to maintaining a balance between supply and demand.While grid storage batteries are currently participating in and monetizing the supply-demand adjustment market, small-scale power storage resources such as EVs and household storage batteries are expected to The role ofaggregator is considered to be important.However, small-scale resources have low per-unit profit and control algorithm development, operation, and maintenance costs must be kept to an absolute minimum. In addition, systems such as supply and demand adjustment markets have complex commodity structures, making it difficult to generate revenue without high-precision control.
Against this background, our laboratory has been studying optimal control methods for storage batteries using reinforcement learning (Reinforcement Learning). Reinforcement learning has the following advantages and is expected to be a next-generation distributed energy management technology:
- Fast inference of learned models, suitable for real-time control
- Automatic adaptation to changes in physical parameters such as storage battery capacity changes and degradation
- Highly reusable and deployable, easily applicable to other DERs (Distributed Generation)
- Quasi-optimal control is possible even with limited computing resources
The research structure for FY2025 includes algorithm development Osone(M2)、 Hashiba(M2)、 Matsuhana(M1)、 Sakurai(B4)will be in charge of this project. Demonstration Tests Hayashi(M1)、 Komatsu(B4)will be in charge of this project.
This research is promoted in collaboration with the following projects and companies:
- NEDO Project(2025-2027):Application of control technology to residential and commercial storage batteries and evaluation under actual conditions
- Data Utilization Project(2025-2026):Training and evaluation of reinforcement learning models using measured data
- Collaborative research with ENERES Co., Ltd.(2024-2026):Applying reinforcement learning to optimize electricity procurement in the retail electricity market to reduce costs and ensure stable supply
Individual research themes
- Optimize EV charging and discharging scheduling to maximize user benefits and convenience [presentation slides]
- Assessing the impact of large amounts of EV charging on distribution grids [presentation slides]
- Probabilistic forecasting of local EV charging demand using machine learning [presentation slides]
- Optimal control of storage batteries and optimization of power procurement strategies using reinforcement learning [presentation slides]
Related publications
- D. Kodaira, “Reinforcement Learning in Action: Optimal Scheduling for Efficient Battery Management,” IEEJ Transactions on Power and Energy, vol. 145, no. 4, pp. 327–330, Apr. 2025, doi: 10.1541/ieejpes.145.327.
- Y. Osone and D. Kodaira, “Quantile Regression for Probabilistic Electricity Price Forecasting in the U.K. Electricity Market,” IEEE Access, vol. 13, pp. 10083–10093, 2025, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3528450.
- M. Cho, H. Aki, and D. Kodaira, “Agent-based power management in apartment buildings: Tenant preferences and distributed energy resources,” Journal of Building Engineering, vol. 96, Nov. 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2024.110563.
- R. Asri, H. Aki, and D. Kodaira, “Optimal management of shared energy storage in remote microgrid: A user-satisfaction approach,” Renewable Energy Focus, vol. 51, p. 100635, Oct. 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.ref.2024.100635.
- H. Yamamoto, T. Kure, J. Kondoh, and D. Kodaira, “Output Forecasting for Multiple Geographically Distributed PVs Without Meteorological Data,” IEEE Access, vol. 12, pp. 86997–87013, 2024, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3412807.
- M. Seo, D. Kodaira, Y. Jin, H. Son, and S. Han, “Development of an efficient vehicle-to-grid method for massive electric vehicle aggregation,” Energy Reports, vol. 11, pp. 1659–1674, Jun. 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.egyr.2024.01.028.
- T. Goto and D. Kodaira, “Optimal Control of Battery System by Reinforcement Learning Considering Profitability,” in 2023 International Conference on Power and Renewable Energy Engineering (PREE), IEEE, Oct. 2023, pp. 12–16, doi: 10.1109/PREE57903.2023.10370554.
Grants (off-campus)
- 1. Optimizing retail electricity procurement,(2025年5月–2026年3月),ENERES Co., Ltd. / Research commissioned by companies:,1,755,000円
- 2. Optimizing retail electricity procurement using reinforcement learning,(2024年12月–2025年3月),ENERES Co., Ltd. / Research commissioned by companies:,650,000円
- 3. Development and demonstration of a general-purpose control algorithm for storage batteries that realizes effective use of surplus electricity,(2023年11月–2024年10月),Amano Industrial Technology Research Institute, Public Interest Foundation / Research Grant:,1,500,000円
- 4. Development and demonstration of a power aggregation model using reinforcement learning,(2023年4月–2025年3月),Japan Society for the Promotion of Science/KAKENHI Grant-in-Aid for Young Researchers:,4,550,000円
- 5. A study on optimal charging algorithms for electric vehicles based on probabilistic demand forecasts,(2021年4月–2023年3月),Japan Society for the Promotion of Science/KAKENHI Grant-in-Aid for Young Researchers:,4,550,000円
Grants (on campus)
- 1. Remote battery charge/discharge control using reinforcement learning,(2024年7月–2025年3月),University of Tsukuba/TIA Collaborative Program Exploration and Promotion Project "Kakehashi":,400,000円
- 2. University of Tsukuba / Support program for continuing and returning to research while balancing childcare and nursing care,(2022年5月),150,000円
- 3. Development of a power aggregation model using reinforcement learning and demonstration in a power distribution system ,(2022年4月–2024年3月),University of Tsukuba/Research Infrastructure Support Program Type S:,2,363,000円
研究テーマの概要

再生可能エネルギーの普及により、電力系統における発電・需要の不確実性が増大しています。このような中、蓄電池を用いた柔軟なエネルギー制御が、需給バランスを保つ鍵として注目されています。現在、系統用蓄電池による需給調整市場への参加と収益化が進む一方で、今後はEVや家庭用蓄電池などの小規模な電力貯蔵リソースを活用するアグリゲーターの役割が重要になると考えられています。しかし、小規模なリソースは1台あたりの利益が少なく、制御アルゴリズムの開発・運用・保守コストを極限まで下げる必要があります。また、需給調整市場などの制度は商品構造が複雑で、高精度な制御を行わなければ収益を得ることが難しいという課題もあります。
このような背景のもと、当研究室では、強化学習(Reinforcement Learning)を用いた蓄電池の最適制御手法の研究に取り組んでいます。強化学習は以下のような利点を持ち、次世代の分散型エネルギー管理技術として期待されています:
- 学習済みモデルの推論が高速で、リアルタイム制御に適している
- 蓄電池の容量変更や劣化といった物理パラメータの変化に自動適応
- 再利用・展開性が高く、他のDER(分散型電源)にも容易に適用可能
- 限られた計算資源でも準最適な制御が可能
2025年度の研究体制としては、アルゴリズム開発を 大曽根(M2)、 橋場(M2)、 松花(M1)、 櫻井(B4)が担当し、 実証実験を 林(M1)、 小松(B4)が担当しています。
本研究は以下のプロジェクト・企業と連携して推進しています:
- NEDOプロジェクト(2025-2027):家庭・業務用蓄電池への制御技術の適用と実環境下での評価
- データ活用プロジェクト(2025-2026):実測データを用いた強化学習モデルの訓練と評価
- エナリスとの共同研究(2024-2026):小売電力市場における電力調達最適化に強化学習を適用し、コスト削減と安定供給を目指す
個別の研究テーマ
- 強化学習を用いた蓄電池制御アルゴリズムでの 物理的制約に基づいた報酬設計 [発表スライド]
- 収益向上を目指した強化学習ベースの蓄電池制御手法の実証 [発表スライド]
- 深層強化学習を用いたPV-蓄電池システムの収益最適化アプローチの提案と検証 [発表スライド]
- Quantile Regressionを用いた 確率的電力価格予測 [発表スライド]
- Probabilistic Forecasting Model for Non-normally Distributed EV Charging [発表スライド]
最適制御に関するテーマ:
予測アルゴリズムに関するテーマ:
関連出版物
- D. Kodaira, “Reinforcement Learning in Action: Optimal Scheduling for Efficient Battery Management,” IEEJ Transactions on Power and Energy, vol. 145, no. 4, pp. 327–330, Apr. 2025, doi: 10.1541/ieejpes.145.327.
- Y. Osone and D. Kodaira, “Quantile Regression for Probabilistic Electricity Price Forecasting in the U.K. Electricity Market,” IEEE Access, vol. 13, pp. 10083–10093, 2025, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3528450.
- M. Cho, H. Aki, and D. Kodaira, “Agent-based power management in apartment buildings: Tenant preferences and distributed energy resources,” Journal of Building Engineering, vol. 96, Nov. 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2024.110563.
- R. Asri, H. Aki, and D. Kodaira, “Optimal management of shared energy storage in remote microgrid: A user-satisfaction approach,” Renewable Energy Focus, vol. 51, p. 100635, Oct. 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.ref.2024.100635.
- H. Yamamoto, T. Kure, J. Kondoh, and D. Kodaira, “Output Forecasting for Multiple Geographically Distributed PVs Without Meteorological Data,” IEEE Access, vol. 12, pp. 86997–87013, 2024, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3412807.
- M. Seo, D. Kodaira, Y. Jin, H. Son, and S. Han, “Development of an efficient vehicle-to-grid method for massive electric vehicle aggregation,” Energy Reports, vol. 11, pp. 1659–1674, Jun. 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.egyr.2024.01.028.
- T. Goto and D. Kodaira, “Optimal Control of Battery System by Reinforcement Learning Considering Profitability,” in 2023 International Conference on Power and Renewable Energy Engineering (PREE), IEEE, Oct. 2023, pp. 12–16, doi: 10.1109/PREE57903.2023.10370554.
助成金(学外)
- 1. 小売電力調達の最適化,(2025年5月–2026年3月),株式会社エナリス/企業からの受託研究:,1,755,000円
- 2. 強化学習による小売電力調達の最適化,(2024年12月–2025年3月),株式会社エナリス/企業からの受託研究:,650,000円
- 3. 余剰電力の有効利用を実現する蓄電池の汎用制御アルゴリズムの開発と実証,(2023年11月–2024年10月),公益財団法人 天野工業技術研究所/研究助成:,1,500,000円
- 4. 強化学習による電力アグリゲーションのモデル開発と実証,(2023年4月–2025年3月),日本学術振興会/科研費若手研究:,4,550,000円
- 5. 電気自動車の確率的需要予測による最適充電アルゴリズムの研究,(2021年4月–2023年3月),日本学術振興会/科学研究費助成事業 若手研究:,4,550,000円
助成金(学内)
- 1. 強化学習による蓄電池の遠隔充放電制御,(2024年7月–2025年3月),筑波大学/TIA連携プログラム探索推進事業「かけはし」:,400,000円
- 2. 筑波大学/育児・介護等との両立のための研究継続・復帰支援事業,(2022年5月),150,000円
- 3. 強化学習による電力アグリゲーションのモデル開発と配電系統での実証,(2022年4月–2024年3月),筑波大学/研究基盤支援プログラムSタイプ:,2,363,000円